Viral infections, toxins, unhealthy lifestyle & large quantity of alcohol consumption are the main causes of fatty liver → chronic liver cirrhosis → liver cancer → death.
|
HES CELL Polypeptides Growth Factors Therapy
· Regulates & balances
a) Endocrine system b) Autonomous nervous system
c) Immune system d) Hemopoietic system
e) Circulatory system f) Digestive systm
· Enhances & increases
a) Natural self – healing power (repair the cells of internal organs)
b) Detoxication effects
c) Anti-inflammatory effects
· Provides vital nutrients for the cells & organs
|
 |
- It contains HGF (Hepato-Growth Factors)
a) Help metabolism & multiplication of the liver cells
b) HGF has good effects on
i) Liver Cirrhosis
ii) Myocardial infarction
iii) Cerebro vascular disease
iv) Renal insufficiency
v) Cancer
After a course of HES CELL Polypeptides Growth Factors Therapy, the SGOT & SGPT will decrease & slowly back to normal. Patient’s general condition will be very much improved eg. more energy, less fatigue, no more numbness of upper & lower extremities, decrease edema, improve appetite…etc.
For liver cancer patients, HES CELL Polypeptides Growth Factors Therapy will prolonged life & improve patient’s general conditions & quality of life.
Liver
1) Regeneration
The liver is the largest vital glandular organ of the body (weight about 1.36kg) and it is also the only internal organ capable
of natural regeneration of lost tissue. As little as 25% of liver can regenerate into a whole liver in within few months.
|
2) Function
a) To produce substance (bile) that break down fat.
b) Convert glucose into glycogen (glycogen storage).
c) Produce urea.
d) Make certain amino acids (the building block of proteins).
e) Filter harmful substances from the blood (detoxification) eg. dead cells, toxins, fats, overabundance of hormones, bilirubin.
f) Hormone production (producing cholesterol, 80% in the body).
g) Decomposition of red blood cells.
h) Storage vitamins & minerals (Vitamin A, D, K, F & B12).
i) Maintain a proper level of glucose in the blood.
j) Produce coagulation factors & insulin – like growth factor & thrombopoietin
|
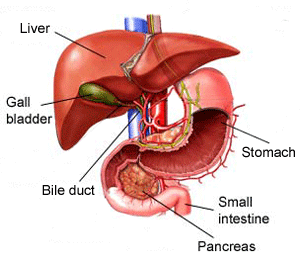 |
3) Disease of the liver
a) Hepatitis b) Liver Cirrhosis c) Fatty liver d) Liver atrophy e) Liver cancer
a) Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by viral infection. The liver is inflamed tender and enlarged, it becomes unable to function normally. As a result, toxin & harmful substances build up in the body and certain nutrients are not processed & stored as they should be. There are 5 main hepatitis viruses responsible for three leading types of the diseases called Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C. The other less common types are Hepatitis D & Hepatitis E & G. All are contagious to some extant. The symptoms of Hepatitis include fever, weakness, nausea, vomiting, headache, loss appetite, joint pain, dark urine, abdominal pain, muscle aches, drowsiness, clay-coloured stools & often jaundice.
Hepatitis A (Infectious hepatitis)
Hepatitis A cause by Hepatitis A virus (HAV) and is easily spread through person-to-person contact, fecal contamination of food & water & raw shellfish taken from polluted water.
Incubation period is 28 days (range from 15 – 50 days). HAV infection produce a self limited disease that does not result in chronic infection or chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis B (Serum hepatitis)
Hepatitis B is caused by infection with Hepatitis B virus (HBV). The viruses are found high concentration in blood & low concentration in body fluid eg. semen, vaginal secretion & wound exudates.
Incubation period is 6 weeks to 6 months.
Transmitted by:-
· sex with infected partner
· sharing needles & syringes
· blood transfusion
· contact with blood or open sores of an infected person
· sharing razors, toothbrushes with infected person
· needle, sticks or sharp instrument exposure
· birth to an infected mother
HBV can survive outside the body at least 7 days and still be capable of causing infection.
Signs & Symptoms
|
Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-coloured stools & jaundice.
In Acute Hepatitis B, the symptoms typically last for several weeks but can persist up to 6 months. Most people 75% recover from Hepatitis B and 25% go on to develop cirrhosis or cancer of the liver.
Acute infection ranges from asymptomatic to mild disease to – rarely – fulminant hepatitis. Disease is more severe among adults age > 60 years. Fatality rate = 0.5% - 1%. Risk of acute to become chronic raises according to the age at infection & is greatest among young children. Approximately 90% of infants, 25 – 50% of children age 1 – 5 years will remain chronically infected by HBV by contrast. Approximately 95% of adults recover completely from HBV infection and do not become chronically infected.
|
|
Treatments
For acute infection – no medication is available; treatment is supportive.
For chronic infection – several antiviral drugs are available eg. adefovir, dipivoxil, interferon alfa-26, entecavir, amivudine…etc. Medical evaluation & regular monitoring is indicated to determine whether the disease is progressing & to identify liver damage or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis C
The most serious form of hepatitis & is the most common chronic blood borne infection in U.S.A.
Acute Hepatitis C infection, the clinical characteristics are similar for all types of acute viral hepatitis. Only serological test is required to meet the case definition.
Person newly infected with HCV are usually asymptomatic. So, acute hepatitis C is rarely identified or reported. Approximate 20 – 30% newly infected with HCV experience fatigue, abdomen pain, poor appetite or jaundice.
Risk of HCV infector:-
1) Blood transfusion
2) Chronic hemodialysis patients or organ transplantation
3) Children born to HCV – positive mother
4) Person with HIV infection
Chances of acute Hepatitis C virus infection turn to chronic.
75% - 85% become chronic
15% - 25% clear the virus from their bodies without treatment. The reasons are not well
known.
Out of 100 patients with HCV infection,
75% - 85% will go on to develop chronic infection.
60% - 70% will go on to develop chronic liver disease.
5% - 20% will go on to develop cirrhosis over a period of 20 – 30 years.
1% - 5% will die from the consequences of chronic infection (Liver cancer or cirrhosis)
No vaccine is available.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Fever, fatigue, dark-urine, clay-coloured stool, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, joints pain & jaundice.
Most chronic HCV patients are asymptomatic. Many chronic liver diseases which range from mild to severe including liver cirrhosis & liver cancer are asymptomatic.
Hepatitis D
Also known as Delta Hepatitis. Is a serious liver disease.
HDV can be acute or chronic, uncommon in U.S.A.
Transmitted through percutaneous or mucosa contact with infections blood or coinfection with HBV or as super infection in person with HBV infection.
No vaccine is available.
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is a serious liver disease cause by HEV that usually result in acute infection. It does not lead to chronic infection. Very rare in U.S.A. but common in many part of the world.
Mode of transmission:-
Ingestion of fecal matter, even in microscopic amount. Out break is always associated with contaminated water supply, countries with poor sanitation. No vaccine available.
Symptoms:
Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark-coloured urine, clay-coloured stool, joints pain, & jaundice.
Most people with HEV recover completely, overall case fatality rate is ≤ 4%. Pregnant women 10% - 30%, particularly those in Third Trimester.
Chronic HEV very rarely appear.
Treatment:
Usually resolves on it own without treatment. No specific antiviral therapy for HEV.
Supportive treatment, advise to rest, adequate nutrition & fluid & avoid alcohol.
Hospitalization for severe cases & pregnant women.
Prevention:
-Good sanitation
-Clear drinking water
|
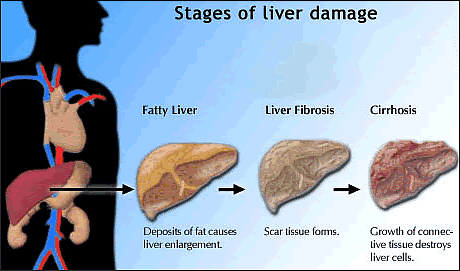
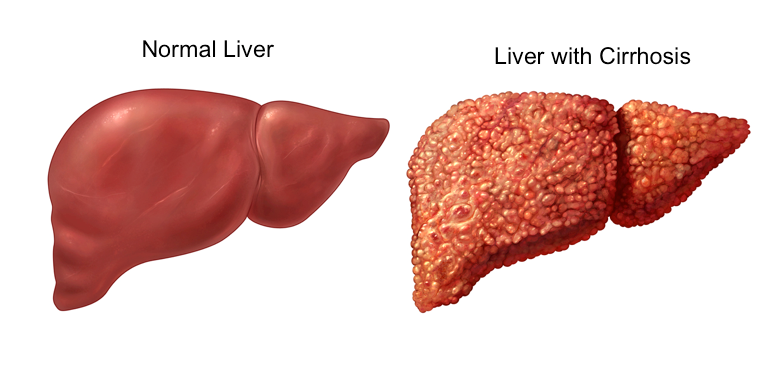
b) Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis of the liver is a slowly progressing degenerative inflammatory disease that results in hardening & scarring of liver cells. The liver becomes unable to function properly.
The most common cause of cirrhosis of liver is excessive alcohol consumption. A less frequent cause of cirrhosis is the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Malnutrition & chronic inflammation can also lead to liver malfunction, others: Fatty liver associated with obesity & cystic fibrosis.
Symptoms of early stage include: constipation or diarrhea, fever, upset stomach, fatigue, weakness, poor appetite, general itching, weight loss, enlarged liver, vomiting, red palm & swelling of the abdomen & legs.
|
 |
Later stage are: develop anemia, bruising due to bleeding under the skin, jaundice & edema.
People with alcohol cirrhosis may experience no symptoms or they may develop very slowly.
|
Signs:
i) Spider angiomata or spider nevi occur in 1/3 of patients.
ii) Palmar erythema
iii) Terry’s nail
iv) Gynecomatia
v) Hypogonadism
vi) Splenomegaly
vii) liver size enlarged or shrunken
viii) Ascites
ix) Caput medusa
x) Jaundice
|
 |
Treatment
Treatment aim is to stop the progress of the cirrhosis & reversing the damage that has already occurred & treating the complications.
a) Consume no alcohol in any form.
b) Avoid most fats.
c) Do not smoke.
d) Proper diet; balance of fatty acid (essential fatty acid).
e) Complete bed rest, restriction of salt intake, plus diuretic when jaundice & ascites present.
c) Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is the accumulation of fat in liver cells. It is also called steatosis.
Causes: i) Chronic Alcoholism & obesity
ii) Starvation
iii) Diabetes Mellitus
iv) Hyperlipidemia
Simple fatty liver usually does not damage the liver.
Symptoms:
i) Patients are often asymptomatic, may have enlarged liver or evaluation of liver enzymes tests.
ii) Loss of appetite
iii) Nausea
iv) Fever
v) Mental confusion
vi) Dry mouth
vii) Weakness, fatigue
viii) Swelling over legs & feets
ix) Abdominal pain & tenderness
Treatment: Treatment is related to the cause.
i) Simple fatty liver may not require treatment.
ii) Strict management of diabetes with diet or insuline lowers blood sugar may prevent further liver damage.
iii) Fat restriction benefit of weight loss & reduce fat in the liver.
iv) Eliminating of alcohol.
v) Controlling elevated levels of cholesterol & triglyceride with diet & exercise or cholesterol lowering medication may help stabilize or reverse non-alcohol fatty liver disease.
d) Liver Atrophy
(Lobar Atrophy, segmental atrophy & acute yellow liver atrophy)
Liver Atrophy – Extensive and rapid death of the parenchyma cells of the liver, sometimes accompanied by fatty degeneration. Also called Rokitan’s Disease. It is a very serious condition. In acute yellow liver atrophy, patient may die 10 days after the diagnosis and 20 days for sub acute yellow liver atrophy.
Treatment:
i) Bed rest and proper nutritions.
ii) Early diagnosis, early treatment for liver atrophy.
e) Liver Cancer
Frequency 3 – 4 times higher in men than in women and most of the patient infected with chronic hepatitis B infection.
Cause: Unknown but definitely induce by chronic liver cirrhosis.
Symptoms: The initial symptoms are variable.
i) Abdominal pain is the most common complain.
ii) Unexplained weight loss.
iii) Ascities, hepatomegaly, liver tenderness
iv) Jaundice
v) Coma → die (in severe cases)
Risk Factors:
i) Hepatitis B infection
ii) Hepatitis C infection
iii) Alcohol
iv) Alfa toxin B
v) Drugs, medications, chemical, toxins
Diagnosis:
i) Blood Test
ii) Imaging study
iii) Liver Biopsy or aspiration
|
Liver cancer grows faster than any other types of cancers. Patient usually dies 6 months after the first diagnosis.
Distant Metastasis
i) Frequent spread to the lung
ii) Can spread to the bone or brain
Treatment: Treatment options are dictated by the stage of liver cancer & the overall condition of the patients.
i) The only proven cure to cancer liver is liver transplantation.
ii) Small tumor → surgical removal (liver resection).
iii) Chemotherapy, chemoembolization, ablation & proton bean therapy all
remain disappointing.
|
 |